The B2B Marketers Guide To Making Google Ads A Better Customer Experience
A marketer’s goal is to create an optimal customer experience. Digital ads, like all forms of content, are part of that customer experience. But it can be difficult to see your ads from customer experience perspective.
There are plenty of online guides available for how to set up ad campaigns. This guide is for marketers who want to understand better what kind of experiences they can deliver through paid ads on Google. You’ll learn what the ads look like to customers, how to choose who sees then and where, and what actions people can take when in response. You’ll also get some tips on optimising and managing your campaign so that you can align customer experience, customer journey and commercial results.
By understanding the different types of customer experiences you can deliver through advertising, and by framing campaigns as part of the customer journey you will be able to devise campaigns that are customer-centric, distinctive, and commercially successful. It’s all about having the confidence to create great campaigns .
Table of Contents
- What Types Of Ads Can Your Customer Experience?
- Previewing Your Ads – What Will Your Customers See?
- Choosing What Your Customers Can Do In Response To Your Ads
- Choosing Where Your Customers Will See Your Ads
- Targeting Who Sees Each Ad
- Keywords – How Will Customers Find You?
- How Do You Know Your Ads Are Working?
- Deep Diving Into Ad Data
- Growing & Learning

What Types Of Ads Can Your Customer Experience?
What Types of Ads Can Your Customer Experience?There are eight different ad types available on Google. It is important to start your ads with a clear understanding of who you are targeting and what you want your audience to do when they see your ad.
Sign up for our newsletter
Get the latest news and ideas from 1827 Marketing sent directly to your in-box.
You will receive an email from us every couple of months, and you can opt out at any time.
Search Ad
A Good Example of a Google Search Ad

Search ads are the most common ad type on Google. They are the ads you see at the top of a keyword search on the Google Search platform.
The ad allows you to have up to 3 headlines of 30 characters, 2 descriptions with 90 characters, and 15 characters for your ad path.
Search ads have three unique extension options.
1 – Site link extensions – internal links to your website visible directly on Google
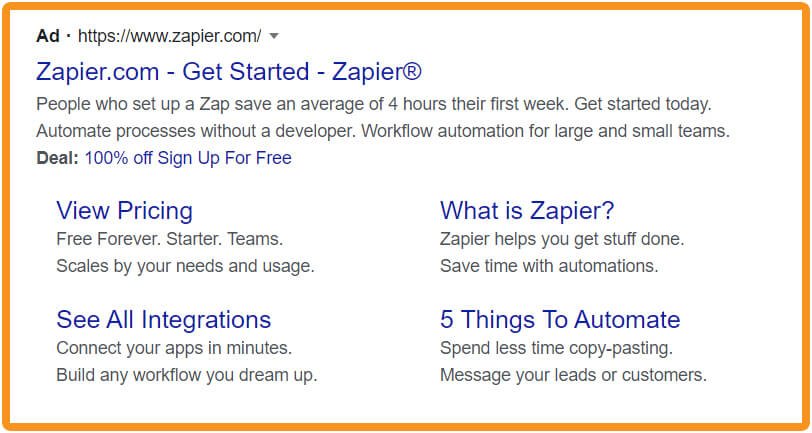
This Search Ad has site link extensions with more options for which pages to visit (and a callout extension offering a deal as well)
2 – Callout extensions – promote unique offers enticing users to click

A search ad with a callout extension offering a free business scan
3 – Call extensions – add your phone number directly on Google
Display Ad

An example of a display ad which appeared on a page in the Financial Times site.
A display ad is a visible version of your ad shared on Google’s display network.
There are two types of display ads. Traditional and responsive. Traditional ads are pre-made images that you upload in different sizes and formats.
Responsive display ads are Google’s way of making sure your ads fit any ad size on any screen. You input an image, logo, and video (if applicable). Create headlines and descriptions. Google will test and optimise your ad to get the best mix of assets.
Shopping Ad
Examples of shopping ads
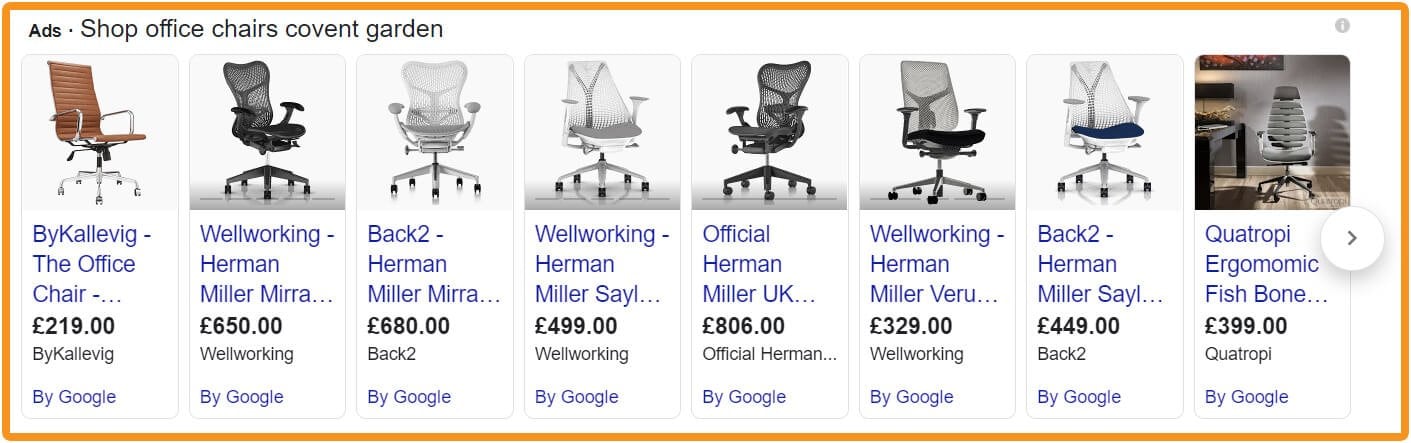
Shopping ads require a Google Merchant Center. The Merchant Center is a product inventory system within Google. You can upload products through spreadsheets, manually, or by connecting to a shop like Etsy or Shopify.
You can segment products by type, tags, and keyword.
You can review your ad group product list before your ads go live and add or subtract products to match your ad segmentation.
A Shopping ad shows up on Google search, in the shopping tab, and on partner sites. They allow your customer to purchase an item without having to leave Google. They also allow a customer to visit your site for more information.
Video Ad
Video ads play a video on the Google Search or Display Network. The video ad will show up in different places depending on the video ad type you choose.
Skippable in-stream ads play before, during, or after other videos mainly on Youtube but can show up on other video platforms
Non-skippable in-stream videos are 15 seconds or less and mainly show on Youtube but can show up on other video platforms
Bumper ads are 6 seconds or less, and viewers can’t skip the ad they mainly play on Youtube but can show up on other video platforms
Video discovery ads only appear on YouTube and appear depending on ad size and format
Outstream ads appear on websites and apps in the Google Display and Search partner network outside Youtube and are only available on mobile and tablet
You can preview what your created video ad will look like to your customers. Click on your video ad campaign, under the ad column hover over the specific ad you wish to view, select preview, then select preview ad on Google.
Smart Ad
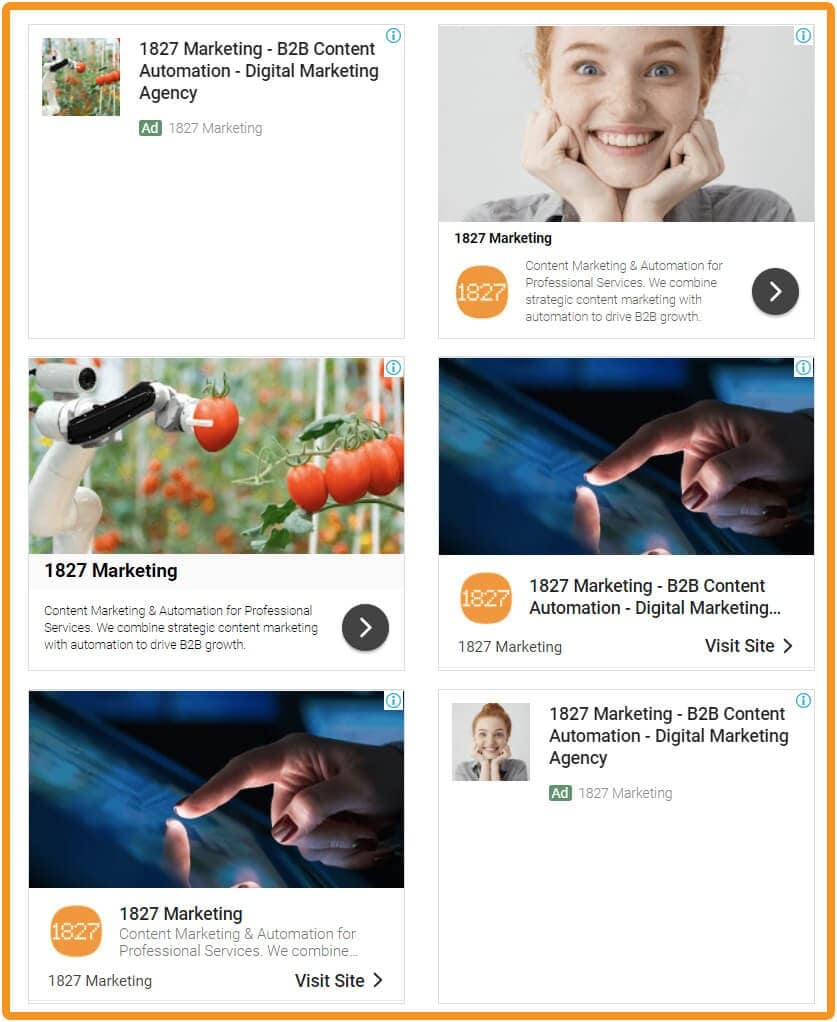
These are previews of Google-Generated Smart Ads, showing how images, headings and descriptions are mixed and matched to create different versions of ads.
Smart campaigns are a way to simplify Google Ads for businesses that are just getting started. A smart campaign only needs an account, website, single ad, category, and budget. The campaign will then learn through conversion goals.
Running a smart campaign gives you limited access to control who and how a customer sees your ads. It is very important to make sure there are only one or two clear goals for a smart campaign.
Smart campaigns do not require the same level of management and time commitment. The ads are meant to learn and grow on their own.
Discovery Ad
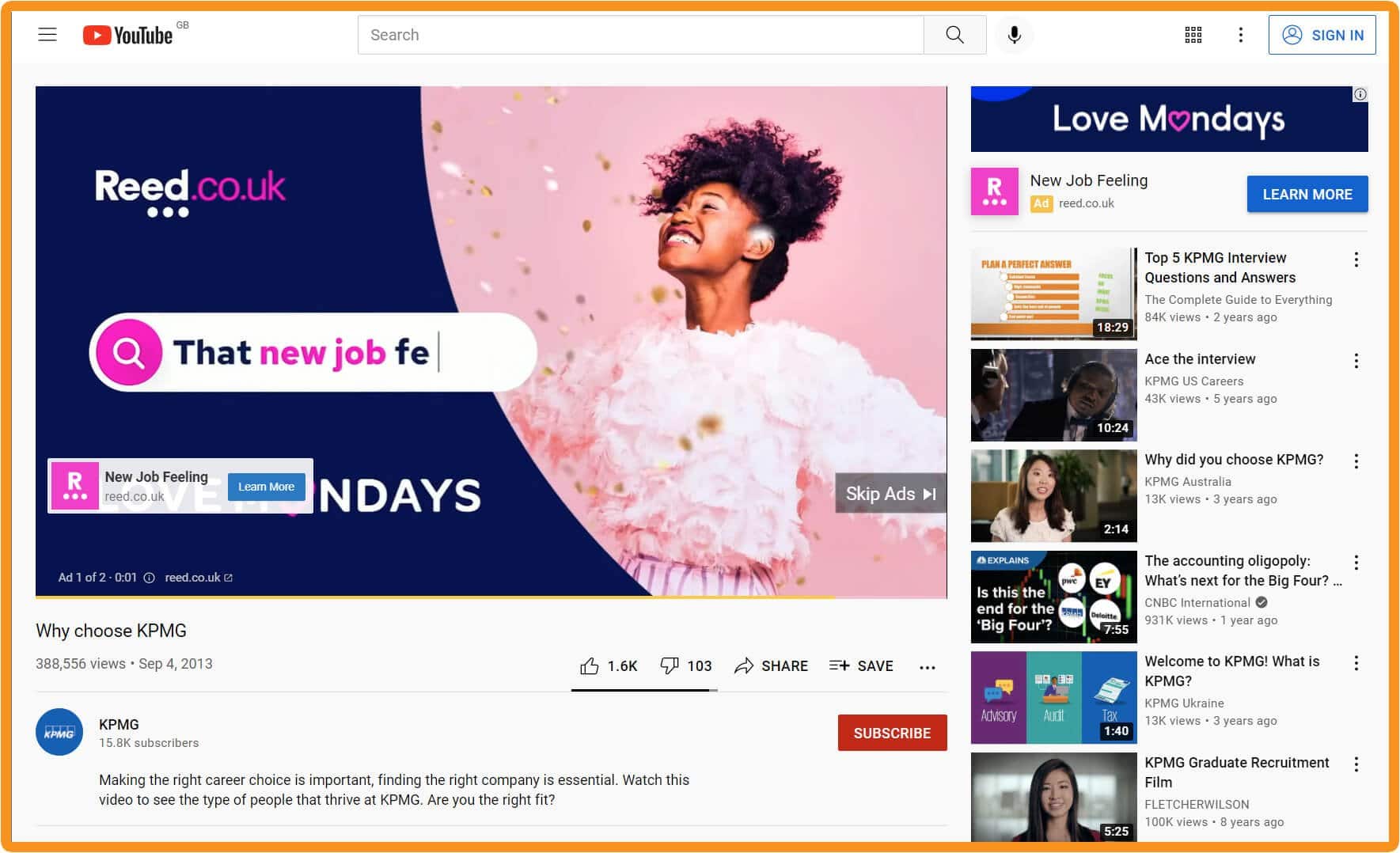
These ads for Reed.co.uk were displayed with a YouTube video for KMPG about career choice – a great example of relevant targeting. Note the display ad in the top-right corner as well as the big video ad that played
Google discovery ads are similar to Facebook Ads. They show up in the Youtube mobile feed and within the Gmail app.
Discovery Ads consist of a 40 character headline, 90-character description, and up to 20 images. The Discover Ad will test the best image for the ad. You can also choose a carousel ad that will use all the images in the ad and let the potential customer scroll through them.
To preview your Discover Ads click on the campaign. Click ads & extensions in the page menu. Select Preview.
App Ads
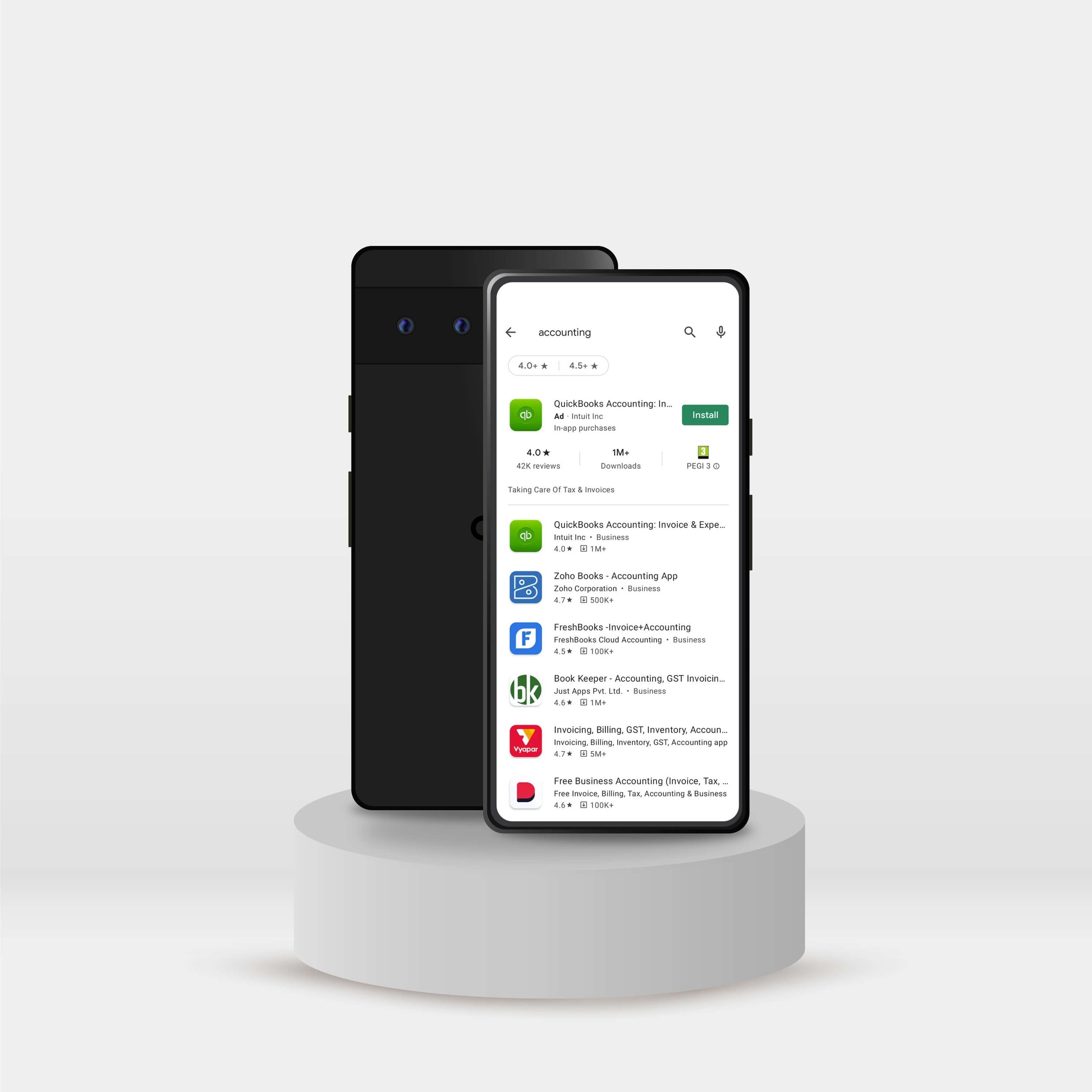
With App Ads, the call to action is to install the app, not to visit a site.
App ads are only available to apps. They show up on the app download page of a mobile phone. They are only available on the Google operating system.
To view app ad previews Google has created a mobile support app. Creative Preview allows you to view mobile-specific ads.
Local Ads
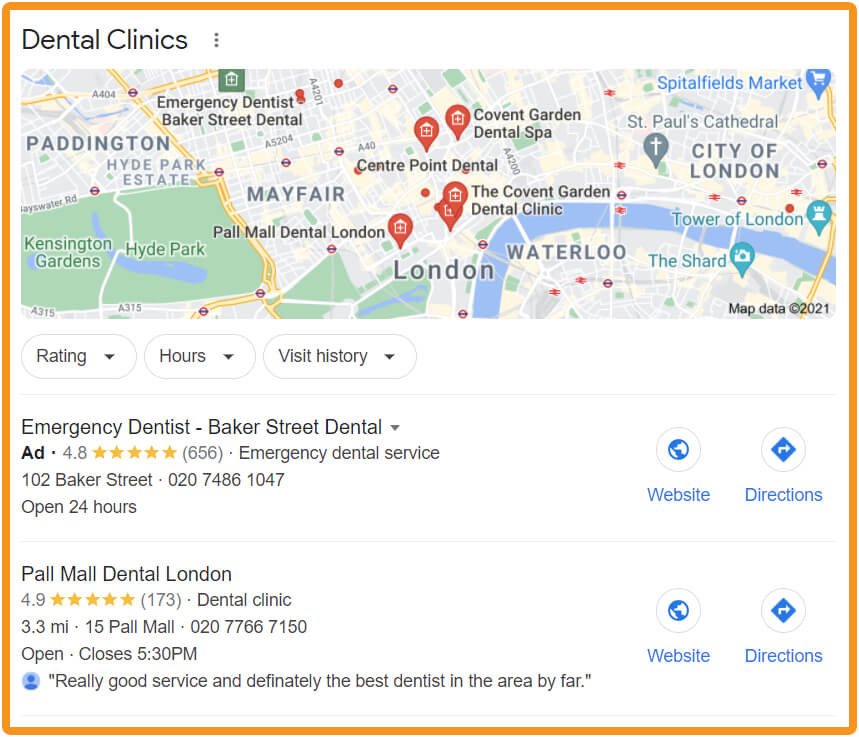
These local ad results can appear when Google sees or discerns ‘near me’ in the search. Note phone numbers, directions, opening hours, ratings and reviews as well as web links.
Local ads are a great feature for a business that services “foot traffic”. Local ads require an active Google My Business (GMB) account with a verified location.
Ads show up in three places. At the top of a related keyword search under a Google verified carousel, on the top of the map pack, and within Google Maps as a visible location.
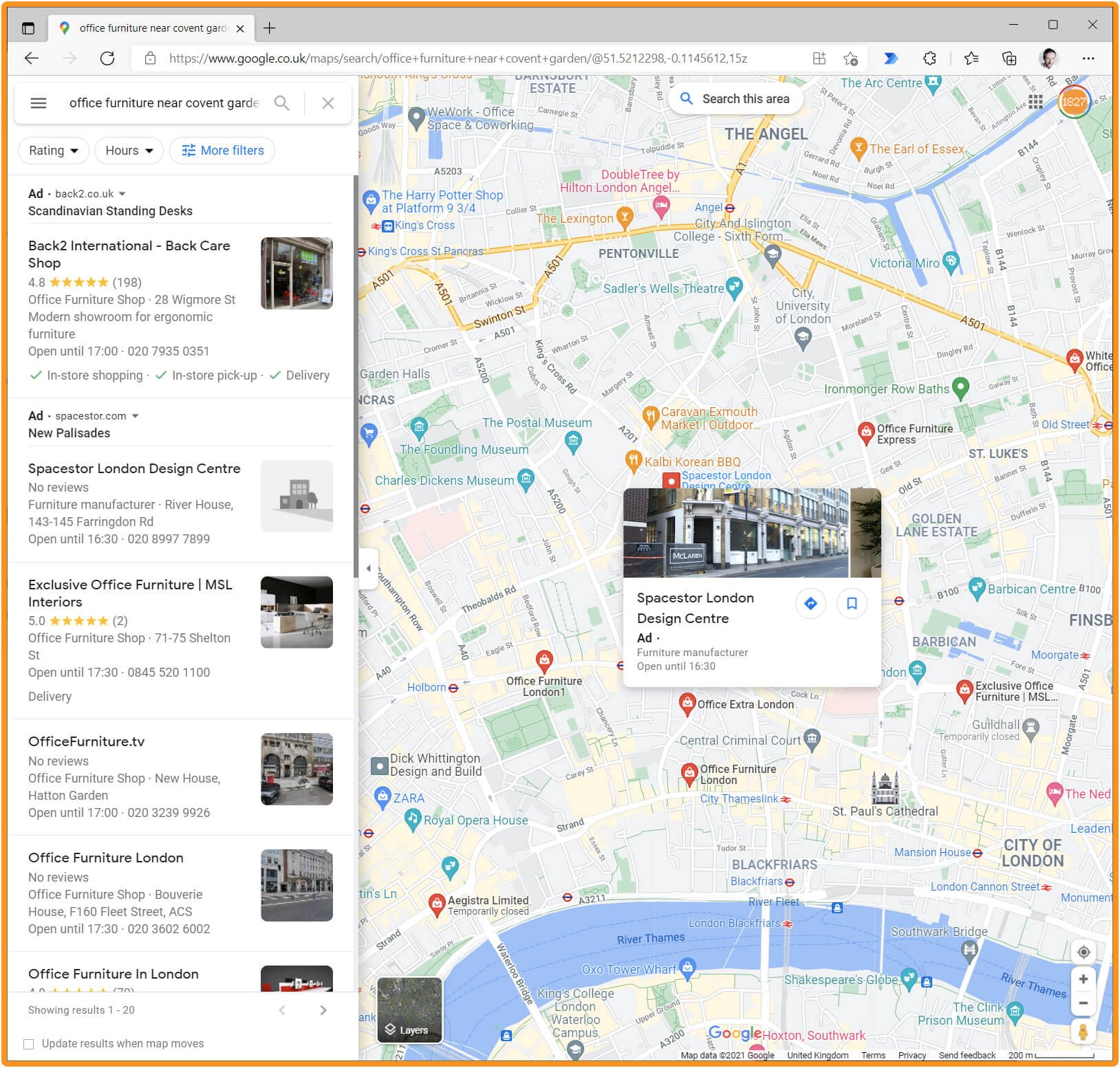
Ads can appear in Google Maps results. Here, you can see Spacestor’s ad in the left-hand column, and also the ad that appears when you click on their location in the map. Directions and bookmarking are available. Other ads on this page use additional ad features.
Local ads work a bit differently Google does not rate these ads on the quality score or click-through rate. Instead, the ad is rated based on location proximity, Google reviews, company response time, and business hours (is your business open when the user is searching).
Previewing Your Ads – What Will Your Customers See?
One of the reasons that we wrote this guide is that you have to go a long way through the process of setting up your ads before you can actually find out what they will look like for your customers. Some of the examples provided in this article should help, but it is (eventually) possible to see previews of your own ads in Google Ad Manager.
You can view ads natively by going to the tool’s section of your account. Click “Planning” then “Ad Preview and Diagnosis”.
You can then play with the settings in your account and search for keywords to see which ad will show for each keyword and ad type.
Choosing What Your Customers Can Do In Response To Your Ads

You should start every campaign by thinking about the action that you would like your customer to take, and then setting a conversion goal that matches it. People often expect that the principle action a customer can take when they see your ad is clicking on it, taking them to your website or landing page.
In fact, Google offers other actions besides clicking to visit a web page. If you choose, your campaign can
encourage customers to call you directly from the ad
provide instant directions via Google Maps to your shop, restaurant, office or salon, or bookmark your location to visit later
download and install your app.
These options allow you to experiment with eliminating different steps and stages from your customer journey to see what works better for your customers and therefor your business. If your the real goal of your campaign is to get customers to call you, why must they visit your site first to find that out? A click-to-call campaign action might make things easier for your customers and in doing so make your campaign more effective.
Choosing Where Your Customers Will See Your Ads
Ad Placement
If you wish you can choose ‘placement’ settings for your ads. This let’s you specify which websites, videos, channels, apps, and app categories that are part of YouTube and the Display Network where you’d like to show your ads.
This can be a great option if you already know your target audience engages with particular sites, or if you want to focus your advertising on sites that have similar values and prestige to your own brand.
You can, of course, explicitly exclude sites that you really don’t want your ad to be seen on. This may be because the sites themselves are low-quality or less than salubrious, or it may be because they conflict with your values or those of your target consumer. As campaigns progress, it’s worth examining where your ads are appearing and refining the exclusion list as you learn more about where your ads are appearing.
Ads won’t necessarily be shown only on the Google Ads network. Google has partnerships with other advertising companies and you can choose to have your ads shown on their networks as well. Unfortunately it’s not possible to choose placement for ads on these other networks.
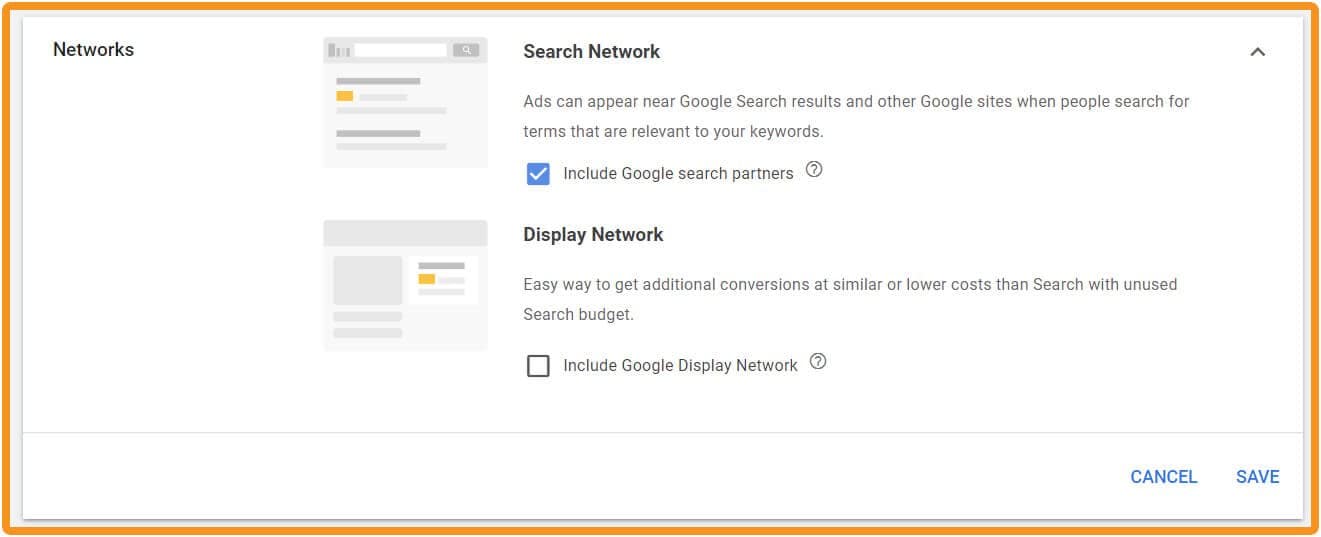
In Google Ad Manager you can choose whether or not to have your ads appear in Google’s partner networks
Who Is In Google’S Search Network?
Google does not have a published list of search partners. Some common sites include ask.com, dogpile.com, lycos.com, and Youtube. Other partners include major retailers like Target, Amazon, and Walmart.
Search partners are sites not specifically connected to Google that also have a search algorithmic system. Search partners can only be turned on or off at the campaign level.
Exclude partner sites and industries that do not service your brand or your customer. Subscribe to Google’s partner site list to keep yourself up to date on any new exclusions you may need to make.
You can use tools like Optmyzr to exclude low-performing search partners.
You can view how Google Search vs. search partners have performed on your ads in your keyword section.
Click the segment view dropdown at the top of your data set and look for “Network (with search partners)”. This will separate out your search ads vs. your search network ads data.
Who Is In Google’S Display Network?
Google’s Display Network is a group of over 2 million apps, sites, and video spots that a Google Ad can show up on.
You can view where your ads have shown up (if you have campaigns that have already been running) under the placements tab of your ad account menu. Click “see where your ads appeared”.
You can exclude the display and search network on all your ads when you set them up. You can also edit the ad group and remove the search and display network after the ad is published.
Targeting Who Sees Each Ad
Choosing who sees your ad is just as important as setting up your ad. There are many ways to segment out a target audience in Google Ads.
Saying who you want to see your ad is one thing, but it is also vital to tell Google who you don’t want to see your ad. Google offers some demographic targeting options, which you will want to combine with more powerful features including online behaviour and purchasing intent.
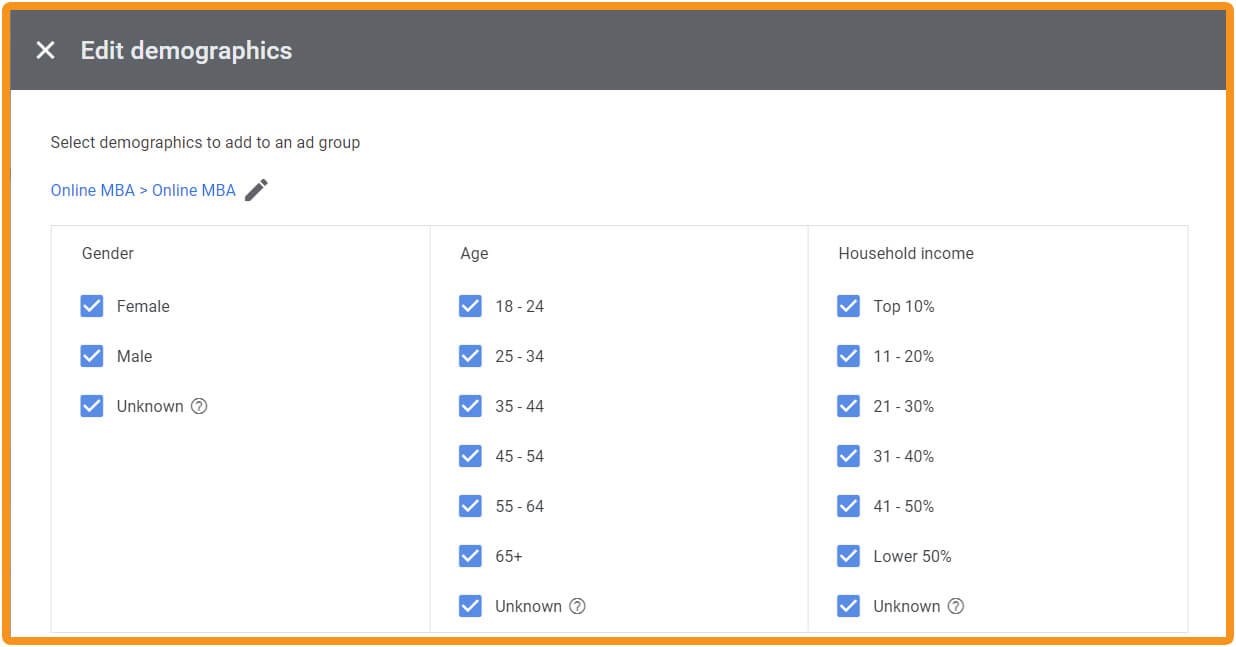
Basic demographics are available to help you target your ads alongside many more sophisticated options based on customer behaviour and intent. It’s not all about keywords.
Location
You can set location targeting for your ad account under account settings. You can target a specific country or city. When you set targeting by cities you can break up the click data later to see which city gets more clicks. You can also see which city has a better cost per click and which city has more completed goals.
You can also set locations for each campaign. Location is set when the campaign is set up. You can also make location changes by editing the campaign.
Language
Language is set at the start of the ad creation process. This can be done for all ad types (except completed video). Language helps Google send ads to people who set their language to the one you have chosen.
Remarketing

Behavioural retargeting and remarketing are great ways to capture the attention of potential customers with an interest in your product or service.
Retargeting ads are set up as their own campaign. You need to have conversion tracking set up on your website. Your retargeting audience can be set up in the audience manager .
Retargeting ads allow you to retarget potential customers that have performed an action on your ads. You can funnel actions through the buyer journey within different campaigns.
Customers that have put products in a cart but not purchased may benefit from a buy now display ad. Customers that have visited the website but did not perform another action may require further enticing on why your product or service should be purchased.
Display ads can be done generically by simply showing a display ad to every website visitor from an ad. They will perform better with a plan. Pick an action your customer took and set up retargeting ad-specific actions and audiences.
Get specific and your conversions will improve. A retargeting audience is a warm audience and is more likely to convert.
Google’S Segments And In-Market Audiences
When it comes to customer intent, Google’s in-market segments are helpful. You can set segments when you set up a new ad group under “edit targeted audience”.
There are several targeting options.
Affinity segments
Life events
In-market segments
Custom segments
Custom intent segments: auto-created (Display)
Your data segments (formerly known as remarketing)
Detailed demographics
Audiences can be set for all ad types at the campaign and ad group levels.
In-Market Segments
These segments cover audiences that are actively searching and comparing products in your niche. This is a great audience that has been vetted by Google to be more likely to make a sale. There are several industries listed under the in-market segment you can choose from.
Keywords – How Will Customers Find You?
It can be daunting to create a keyword list. Lots of articles recommend methods that feel tricksy and obscure, and this just increases marketers’ anxiety that they’ll be getting it wrong somehow. Our advice is to think like your customers and use the everyday words that you know they would use when looking for your services.
Google can help. Google builds keyword lists in the Keyword planning tool or allows you to run smart campaigns.
Smart campaigns run on keyword themes. This is a great way to easily manage a new ad account when you have limited resources or knowledge of Google Ads.
If you want more control over your keywords under the advanced tab Google’s Keyword planner can help you set up your first keyword list. To find the keyword tool click tools & settings and keyword planner under planning.
As the campaign matures and you can see from the campaign data what people are responding to, you can hone in on the keywords that work best for you and your customers in that campaign.
Keyword ‘Themes’
Keyword themes are used in smart ads. The themes allow you to pick one central keyword that covers every relevant term to that keyword.
The theme word is usually an important keyword in your industry. For example “plumbing” would be a keyword theme. Google will then add keywords like “plumbing near me”, “local plumbing”, and “plumbing services” under the main keyword.
Helping you add main keywords to a list without having to add every conversion-based related keyword.
Themes can only be used in smart campaigns.
Negative Keywords
Negative keywords are the keywords you don’t want your ads to show up for.
Negative keywords are just as important as keywords. They help improve your click-through rate and lower ad costs by removing irrelevant traffic.
To find your negative keywords under the keyword drop-down in your ad menu click negative keywords. It is a good practice to check this section once a week or less. That will help get rid of any keywords you may be paying for that will not get you a sale.

How Do You Know Your Ads Are Working?
Having the right goal set up on your ad will help you understand if customers are performing the action you want. If you want sales, make sure that you are tracking a goal that relates to checkout on your online store. If you want white paper downloads, make sure you’re tracking either the download link or the thank-you page. Similarly, if want meetings, make sure you are able to track when meetings have been booked.
The more specific you are about the online action that corresponds to your commercial objective, the better your campaigns will be.
Be very clear about your ad conversion goal. Google will optimise your campaign to your conversion goals.
Ads optimize based on conversion goals. If you set more than one goal Google will think your ads are performing, while you may disagree.
Conversion goals can be set at the campaign level. You can set “ consideration goals ” which are goals that are only there for data capture purposes.
Deep Diving Into Ad Data
You know you have to optimise your ads, but it can be difficult to understand where to look when optimising your ads.
There are 4 metrics to guide optimisation on search ads.
Quality Score
A quality score is calculated using three quality metrics. Expected click-through rate, ad relevance, and landing page experience. This score lets Google know how relevant the ad will be to a specific search experience.
The quality score plays a large role in deciding where your search ad will show up on the search result page and how much that ad will cost you. A better quality score will lower your ads cost per click (CPC).
You can find your ad quality score by visiting the keyword section of your ads. To view your quality score click columns on the right-hand side of the screen and modify columns. Under the quality score drop-down, turn on:
Quality Score
Exp. CTR
Landing Page Exp.
Ad Relevance
Maintaining your quality score between 7 and 10 and following Google’s advice for optimisation will deliver more prominent ads at a lower cost, improving your account’s return on ad spend (ROAS).
Expected Click-Through Rate
Expected Click-Through Rate is calculated using clicks and impression data. There are four main ways to start improving this metric.
Add relevant negative keywords
Improve copy to be more relevant to your keyword
Improve the keyword and add relevance
Improve the search term
Landing Page Experience
Directly relates to your landing page performance. This includes load time, after ad CTR, mobile responsive, CTA, and keyword prevalence.
Your customer should know exactly what to do when they click on your ad.
Ad Relevance
Ad relevance is calculated by how closely your keyword matches your ad copy.
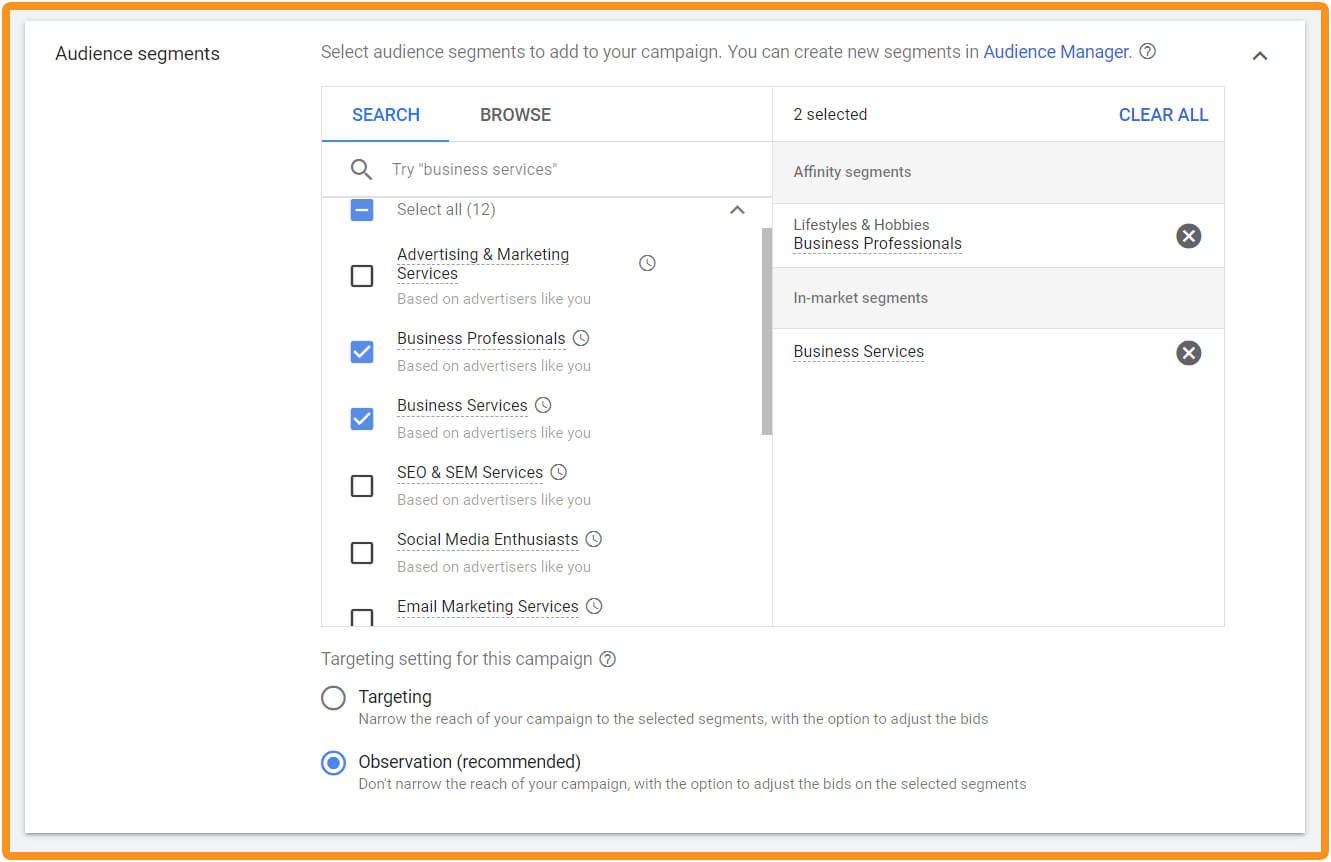
Google offers the ability to target your ads based on what it has observed about its own users such as their interests, lifestyle and hobbies. More importantly, Google can identify who might be actively looking (‘in market’) for services like yours.
Growing & Learning
As a marketer, you’re focused on results but, you also need to focus on the customer experience. Here are the three top takeaways from this article.
Define Conversion Goals
Google needs a clear goal. The goal helps Google promote ads to people that perform the action you want. It is important to be precise in setting your conversions.
Impressions and visits are nice, but your conversions should be actions that are valuable to your business like making a sale, getting a meeting, or starting a trial. Tell Google what valuable thing you want to happen, and it will optimise for that.
You can set a few different goals for your ads.
Sales
Leads
Website Traffic
Product and Brand Consideration (Video-based brand awareness)
Brand Awareness and Reach (Display and video brand awareness)
App Promotion (app downloads)
Local Store Visits and Promotions (Local Ads)
Each ad conversion goal allows you to use certain Google ad types. Google sets these rules based on data. They know what a customer is likely to do when they see each ad format.
You can set up campaigns without a conversion goal. It is not advised unless you are an advanced Google Ad specialist.

Use Your Analytics
Pay attention to what Google Analytics is telling you. Use the goals you have set along with quality score and keyword performance to continue to improve your ads over time.
Keep using negative keywords to create more focus in your ad campaigns. Adjust your budget when necessary. Your campaign might start off out of shape, but with work and learning, it can be improved.
Know Your Customers
Ads are part of your overall digital brand experience. Know what your ads like and feel like to your customers. Follow your customer journey. Make sure you are being clear on the goal of your ads without restricting the journey.
You can also check out our article on how ad insights can shape your content strategy.
We believe content is part of your customer experience, delivering a great advertising experience can help you improve that experience.
Book a demo if you want to talk about our online advertising services or your Google Ads.
Have a B2B marketing project in mind?
We might be just what you’re looking for






